Need to convert hex to text?
Hexadecimal notation is used as a human-friendly representation of binary values in computer programming and digital electronics. Most programming languages such as Java, ASP.NET, C++, Fortran etc have built-in functions that convert to and from hex format.
What is a Hexadecimal?
Most people are familiar with the decimal, or base-10, system of numbers (all possible numbers can be notated using the 10 digits, 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9). With only 10 digits, extra digits need to be used at certain intervals to correctly notate a number. For example, the number 423,004 uses twice as much digits as the number 961.
The hexadecimal, or base-16, system was created to emulate some of the same properties of the common decimal system. The overall difference is, 16 digits are available instead of the 10 digits available to use to notate the value of a number.
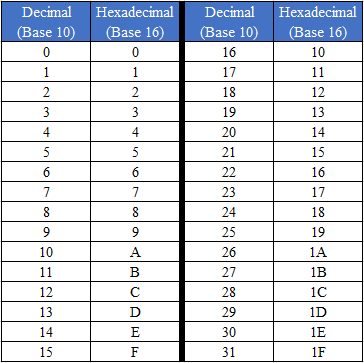
The 16 symbols that the hexadecimal system uses are: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E and F. So instead of a decimal symbol of 10, hexadecimal uses an A, and so on and so forth until we get to the decimal of 15 which is notated as F. Similar to the decimal system, after the base of 16 symbols has been used, the appropriate extra digit is added and the order of numbers starts over. In other words, after F, we begin with 10, and so on. To better understand the relationship between the Decimal and Hexadecimal system, check out the table below.
How is Text to Hexadecimal Encoding Used in Programming?
Hexadecimal encoding is used by programmers to improve readability of bytes, which are used to communicate to computers. There are a number of benefits for using hexadecimal encoding, including the the higher information density available, as hexadecimal encoding effectively reduces 8 digits of binary code to 2 hexadecimal digits. With this effect, 2 hexadecimal digits expresses any number from 0 to 255, the same scope of numbers as binary’s 8 digits.
Text to Hex Encoding vs. Base 64
While Encoding in Hex is a popular encoding strategy used by progammers, Hex encoding does significantly increase the space used of storage, which reduces the efficiency of your communication with the computer. If storage space is an issue, encoding in Base 64 is recommended as an alternative.
What Is Hex Encoding Used For?
The reasons for using hex encoding are basically the same as for Base64 encoding - it's used for when you want to send or store 8 bit data on a media that only accepts 6 or 7 bits. Hex encoding is performed by converting the 8 bit data to 2 hex characters. The hex characters are then stored as the two byte string representation of the characters.
Often, some kind of separator is used to make the encoded data easier for human reading. With 8 bits converted to three characters and each character stored as 1-4 bytes you might use up to 12 bytes (or even more in some cases) for each byte of information.
Again, don't use hex encoding if storage space is an issue. The encoding is quite easy to read though, so if human readability is an issue, then hex encoding is probably a better choice than base64 encoding.

How to Use The Free Hex Encoding Tool
The above String to Hex Converter is verty simple to use. Enter or paste the code you would like to convert to hexadecimal, and then click Convert below the paste area. Encoded string will appear in the box below, where you can easily copy it from. For your ease and efficiency, we recommend bookmarking this tool for future use.
String Functions also has created a free online tool to convert hexadecimal back to text. Try it today!

Privacy Policy Sitemap
Keywords: hex decode endoce a string text, tool, on line, tech career tool, decoder.